Unfortunately it has nothing to do with chocolate cake…A Baker’s cyst is a collection of fluid that accumulates in the back of the knee. It typically occurs from one of three different sources.
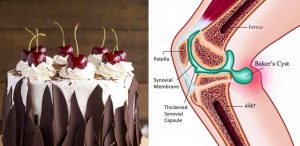
1. The most common reason people develop a Baker’s cyst is from osteoarthritis. If you have an arthritic joint that gets inflamed, and is in the inflammatory stage, it produces fluid. The fluid can leak out of the knee joint and accumulate in the back (posterior) part of the knee outside of the actual knee joint.
2. The second source of a Baker’s cyst is a tear of the meniscus. When you have a meniscal tear fluid can leak out of the knee joint. It creates a one way valve where fluid leaks out and cannot get back into the knee joint. Therefore it collects and forms a cyst.
3. You can also have a tear in one of your tendon sheath that surrounds your hamstring tendons and fluid can leak out in that area and create a Baker’s cyst as well.
Can Baker’s cyst get bigger and smaller?
Yes, if your arthritis goes into a non-inflammatory stage. When the knee joint produces less fluid, the baker cyst will get smaller and sometimes completely resolved. Baker’s cysts can also get so big that they rupture on their own. If you have a meniscal tear and you undergo surgery, the bakers cyst tends to go away on its own.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Can a Baker’s cyst become malignant or cancerous? – No
2. If a Baker’s cyst is drained will it come back? – Yes, you must stop the source of the fluid that’s creating the Baker’s cyst. Simply draining the cyst with a needle will decompress the cyst for a short period of time typically less than 24 hours and then the fluid will accumulate again. If you have arthritis, reducing the inflammatory phase of the arthritis will reduce the size of the Baker’s cyst. If you have a meniscal tear, having a knee arthroscopy will eliminate the Baker’s cyst.
3. Can a Baker’s cyst be surgically removed? – Yes, but they tend to come back very quickly if you don’t stop the source of the fluid that is causing the bakers cyst to occur.
4. What is inside of a Baker’s cyst? – Synovial fluid, located inside of your knee joint that helps to lubricate your knee.
5. Will you remove the Baker’s cyst at the time of a knee arthroscopy which is being done for a meniscal tear? – No, the Baker’s cyst is actually located outside of the knee joint and outside of the capsule of the knee. You cannot access the Baker’s cyst from the inner part of the knee joint while doing a knee arthroscopy. By resecting the meniscal tear the Baker’s cyst typically will go away.

Recent Comments