Key Takeaways:
- Traditional shoulder replacement surgery is done for patients with shoulder arthritis who have an intact rotator cuff.
- Reverse shoulder replacement surgery is done for patients with shoulder arthritis who do not have an intact rotator cuff.
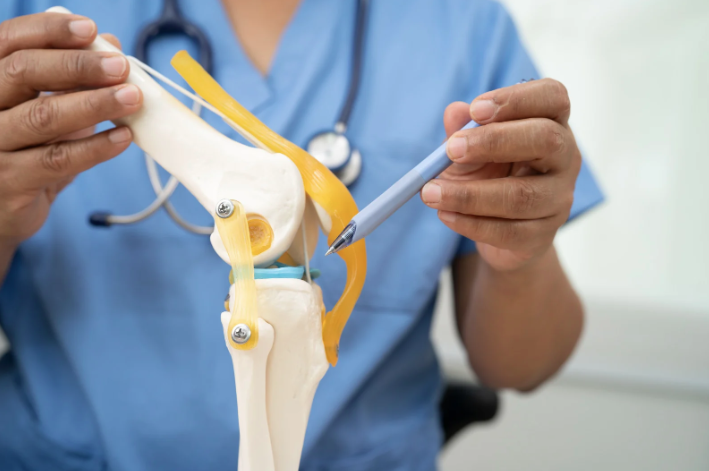
- In a shoulder replacement surgery, the glenoid sphere is connected directly to the humeral shaft whereas in a reverse shoulder replacement, the glenoid sphere is connected to a glenoid, and then the humeral shaft.
Reverse shoulder replacement and traditional shoulder replacement offer shoulder pain relief for many patients. In fact, more than 100,000 people in the United States choose shoulder replacement surgery each year (Yale Medicine).
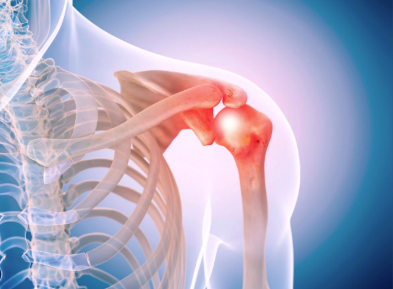
Shoulder pain often starts when arthritis damages joint cartilage or when the rotator cuff weakens. The shoulder is a ball-and-socket joint that depends on smooth cartilage and strong muscles. When cartilage wears away, movement becomes painful and restricted. Rotator cuff damage further limits strength and stability. These problems affect many adults, especially those over age 60, athletes, and manual workers.
If possible, non-surgical care always comes first. Physical therapy can improve strength and flexibility, while medications and injections can reduce inflammation and pain. However, these options sometimes stop working or don’t work at all for certain conditions.
After non-surgical options run out, surgery then becomes the recommended next step.
What are the Key Differences Between Shoulder Replacement Types?
Choosing the right surgery depends on joint damage and rotator cuff health. Traditional shoulder replacement copies natural anatomy. The artificial ball attaches to the upper arm bone, and the socket attaches to the shoulder blade. This option works best when the rotator cuff functions well.
Reverse shoulder replacement changes the joint structure. The ball attaches to the shoulder blade, then the socket attaches to the upper arm bone. This design allows the deltoid muscle to power arm movement. Reverse shoulder replacement works well when the rotator cuff is torn or nonfunctional.
Common conditions treated with reverse shoulder replacement include:
- Chronic rotator cuff tears
- Severe shoulder arthritis with weakness
- Rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory joint disease
- Complex fractures
- Failed previous shoulder surgery
Many patients with these conditions regain overhead motion within weeks.
What to Expect From Shoulder Replacement Surgery
Both surgeries usually take less than two hours, and most patients go home the same day or after one night.
Procedure: Surgeons often use 3D imaging to plan precise implant placement. Additionally, muscle-sparing techniques help protect surrounding tissue for the best results.
Pain Control: Pain control includes general anesthesia and nerve blocks. These methods work to reduce discomfort and limit opioid use so that patients don’t need to worry about developing a reliance on them.
Recovery: Recovery starts with light daily activities combined with guided rehabilitation. Physical therapy usually lasts about 12 weeks, and most patients reach overhead by three months.
How Long Will My Shoulder Replacement Implant Last?
Modern shoulder implants last several years. Over 90% still function well after ten years, especially now that surgeons use durable materials like titanium and polyethylene. New options include pyrocarbon components and patient-specific implants, which further advance the fit, movement, and longevity.
FAQs About Shoulder Replacement Surgery
- What makes reverse shoulder replacement different from traditional shoulder replacement?
It reverses the joint structure and uses the deltoid muscle instead of the rotator cuff. - Who benefits most from reverse shoulder replacement?
Patients with severe rotator cuff damage or limited shoulder mobility benefit most. - How long does recovery take?
Most patients improve steadily over three to six months with physical therapy. - How long do shoulder implants last?
Most implants function well for at least ten years or longer. - When should I consider surgery?
Surgery may help when pain and stiffness prohibit your daily activities, even after conservative care.
If you or someone you love has suffered a shoulder injury in the Louisville, Kentucky-area, board certified sports medicine physician Dr. Stacie Grossfeld at Orthopaedic Specialists PLLC can help. Orthopaedic Specialists PLLC is accepting new patients, and same day appointments are available. For additional information or to schedule an appointment, please contact Orthopaedic Specialists PLLC today at 502-212-2663.



Recent Comments