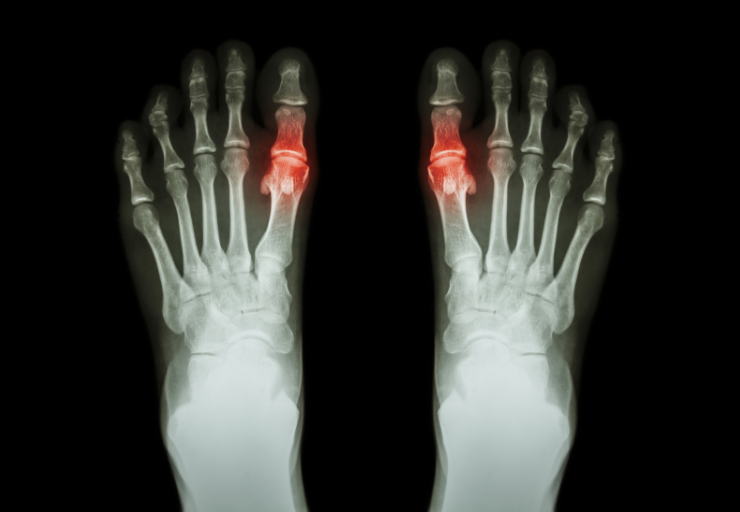
Gout and pseudogout are two conditions that have a lot of similarities. But how are they different? Are they different? Despite sounding alike and having similar symptoms, the two are different! There are a few key differences between them that can be difficult to pick out. In fact, it would take a microscope to know for sure which is which.
Gout is caused by hyperuricemia (too much uric acid in the body). Pseudogout is a condition known as calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease (CPPD). In simple terms, gout and pseudogout develop due to different types of crystals in the joints.
Causes of Gout vs Pseudogout
The different types of crystals that form in the joints are the physical causes of gout and pseudogout. Gout is the result of sodium urate crystals that appear in and around joints. They form due to high levels of uric acid. Uric acid is your body’s natural method of breaking down purines in foods and the body. But when there is an overproduction of uric acid, it crystalizes and builds up in joints, fluids, and tissues within the body and produces the inflammation and joint damage that characterize gout. Obesity, insulin resistance, high cholesterol, heart disease, hypothyroidism, and kidney disease have been associated with gout.
Pseudogout is the result of calcium pyrophosphate crystals (CPP). These crystals form and build up in the joint cartilage. Unlike uric acid, it is unknown why CPP crystals form. However, excess iron or calcium, low magnesium, an abnormal thyroid gland, or a genetic predisposition may be contributing factors.
Symptoms of Gout and Pseudogout
The symptoms gout include a sudden and severe arthritic attack characterized by a red, hot, swollen, and painful joint. After the attack is over, people with this conditions experience no symptoms at all, so it is difficult to anticipate the next. While it can affect any joint, over 50% of gout cases occur in the big toe, with the ankle, lesser toe joints, and knees also common sites of inflammation. Gout also usually only affects one joint.
This differs from pseudogout, which has a higher chance of affecting multiple joints, usually the knees. The symptoms are almost identical to gout, with joints becoming red, swollen, and warm during the sudden and severe attacks.
Diagnosis of Gout and Pseudogout
As mentioned before, you would have to use a microscope to differentiate between CPP crystals and sodium urate crystals. A common way that gout and pseudogout are diagnosed is via fluid that is drawn from around an affected joint and then analyzed. However, gout diagnosis usually relies on your history of arthritic attacks along with exam findings, since some people who experience gout have low uric acid levels at times. CPPD is diagnosable via MRIs, ultrasounds, CT scans, and X-rays on top of lab tests.
Treatments for Gout and Pseudogout
Gout and pseudogout have different treatments, despite the symptoms being so similar. Gout is treated with a unique combination of dietary and lifestyle modifications and medication. The different medications include:
- Drugs to ease inflammation:
- Colchicine (Colcrys)
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Glucocorticoid (steroid) pills or shots
- Drugs to lower uric acid in the blood to the recommended 6ml/dL level:
- Allopurinol (Zyloprim)
- Febuxostat (Uloric)
- Drugs that help the kidneys remove excess uric acid:
- Probenecid (Benemid)
- Lesinurad (Zurampic)
- Pegloticase (Krystexxa)
Pseudogout has less treatment methods available, since much about the disease is still unknown. There is no way to dissolve the calcium pyrophosphate crystals, but there are ways to manage the pain. Common treatments include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to treat joint pain and swelling
- Draining fluid from affected joints
- Corticosteroid injections
- Drugs like methotrexate, colchicine, or the interleukin beta-1 antagonist anakinra (Kineret)
- Surgery to repair or replace damaged joints
Gout and Pseudogout Treatment in Louisville, KY
Gout and pseudogout are painful conditions to live with. Diet and lifestyle may help mitigate the effects, but sometime medical intervention is necessary. Orthopaedic Specialists specializes in joint pain and pain management. If you need a corticosteroid injection or joint surgery, contact board-certified orthopedic surgeon Dr. Stacie Grossfeld today!
If you or someone you love has suffered an injury in the Louisville, Kentucky-area, board certified sports medicine physician Dr. Stacie Grossfeld at Orthopaedic Specialists PLLC can help. Orthopaedic Specialists PLLC is accepting new patients, and same day appointments are available. For additional information or to schedule an appointment, please contact Orthopaedic Specialists PLLC today at 502-212-2663.

Recent Comments